Mean Squared Error - method variability testing and system tuning.
Mean Squared Error (MSE) is a process in which you determine the determine the difference between observed values and their arithmetic mean, square each difference, then sum the squares. The size of the SME tells you how good of an estimate the set point likely is. The arithmetic mean of a sample set always produces the lowest MSE against that sample set.
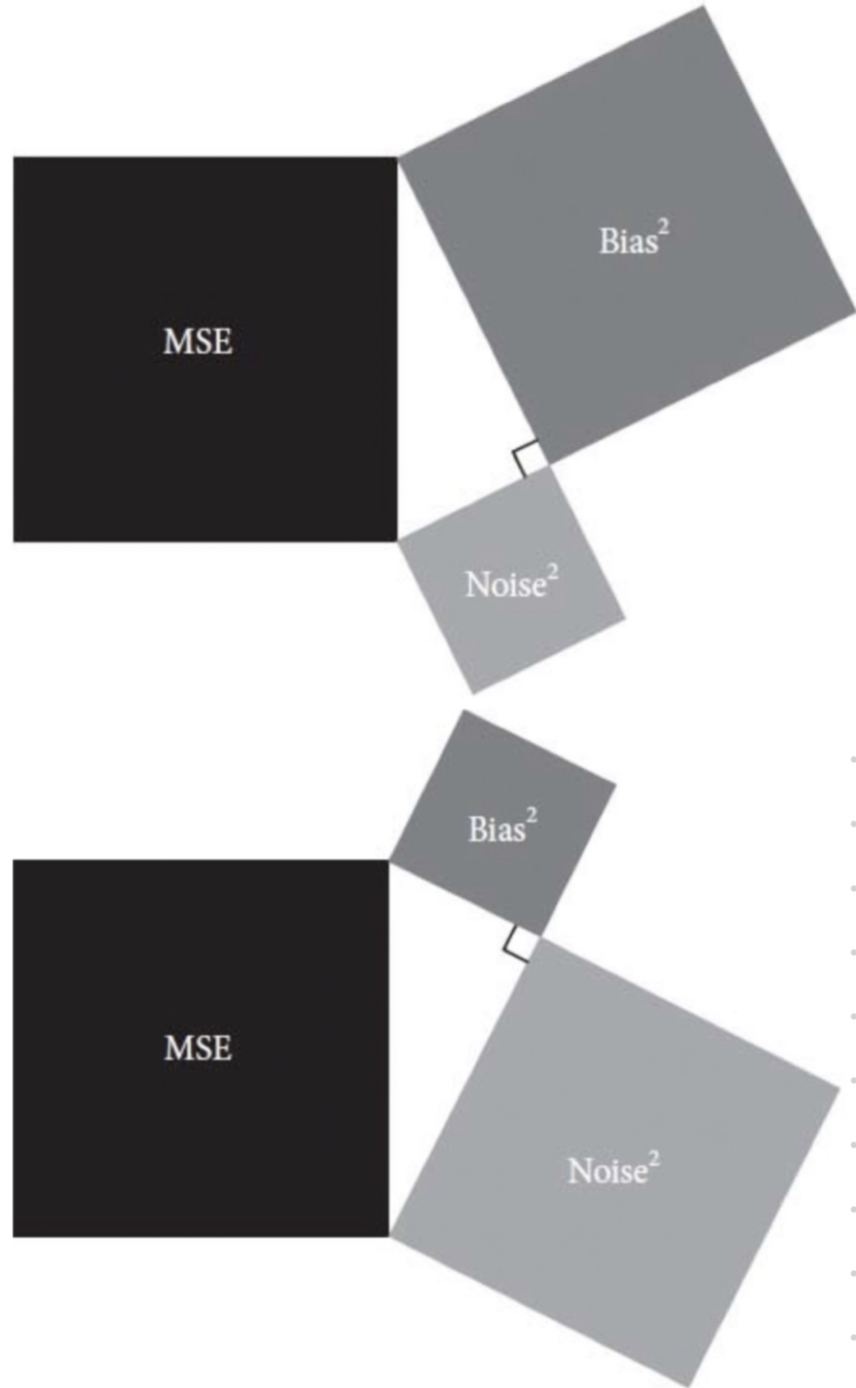
Alternatively, if the measurements are assumed valid representations of members of a population, the size of the MSE is a measure of variability of the given trait within the population.
MSE is also used in Regression Testing.
Example
For the dataset: [7, 9, 9, 11, 14]
- Mean: 10
- Median: 9
- Mode: 9
- MSE Checks:
- 9 ⇒ 33
- 9.5 ⇒ 29.25
- 10 ⇒ 28
- 10.5 ⇒ 39.25
- 11 ⇒ 33